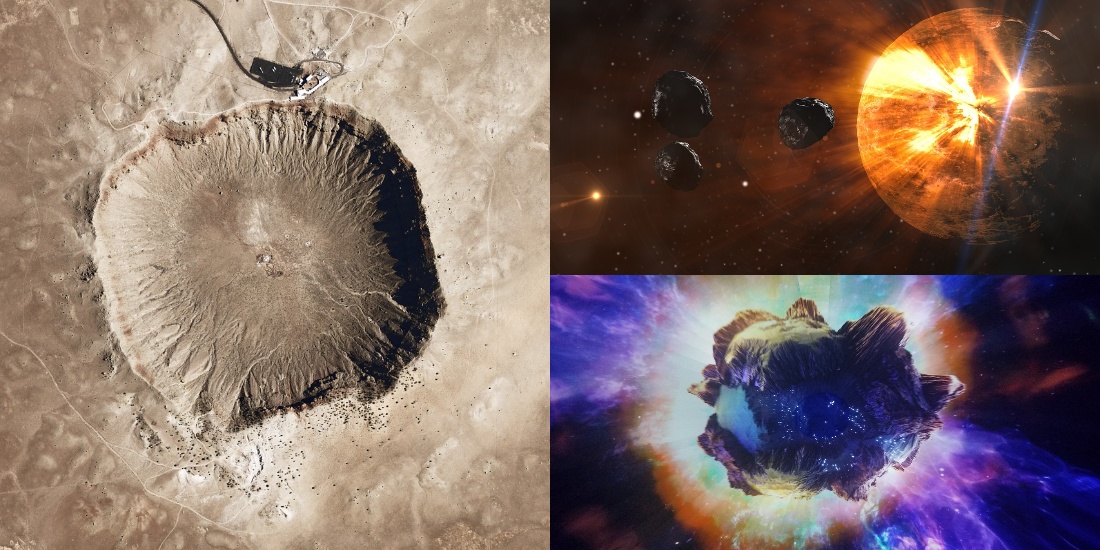
Meteors retain several distinct characteristics that make them interesting and distinguish them from other Elysian objects. Then are some crucial characteristics of meteors-
Appearance- Meteors frequently appear as bright stripes of light, generally appertained to as” shooting stars.” They generally have a quick and flash nature, lasting only a many seconds or lower as they cut the sky. The brilliance of a meteor can vary, ranging from faint to extremely bright, with some meteors being seen indeed in daylight.
Speed- Meteors travel through Earth’s atmosphere at high rapidity, generally ranging from 11 to 72 kilometers per second( 25,000 to 160,000 long hauls per hour). The speed of a meteor depends on colorful factors, including the haste of the parent meteoroid, its angle of entry, and atmospheric conditions.

Brilliance- Meteors can vary in brilliance. While some meteors may be fairly faint and delicate to observe, others can be incredibly bright, competing with or indeed surpassing the brilliance of the brightest stars in the sky.
Incandescent Train- As a meteoroid interacts with the atmosphere and heats up due to disunion, it creates a glowing trail known as an incandescent train. This trail is visible for a short period behind the meteor and frequently persists for many seconds indeed after the meteor has faded from view.
Duration- The duration of a meteor’s visibility in the sky can range from a bit of an alternate to many seconds. Some bright meteors may persist for a longer period before fully burning up or disintegrating.
Colors- Meteors can parade colorful colors, primarily grounded on their composition. utmost meteors appear white or unheroic, but some may display tones of green, blue, or indeed red. The colors arise from the luminescence of the vaporizing meteoroid and the ionized gas in the meteor trail.
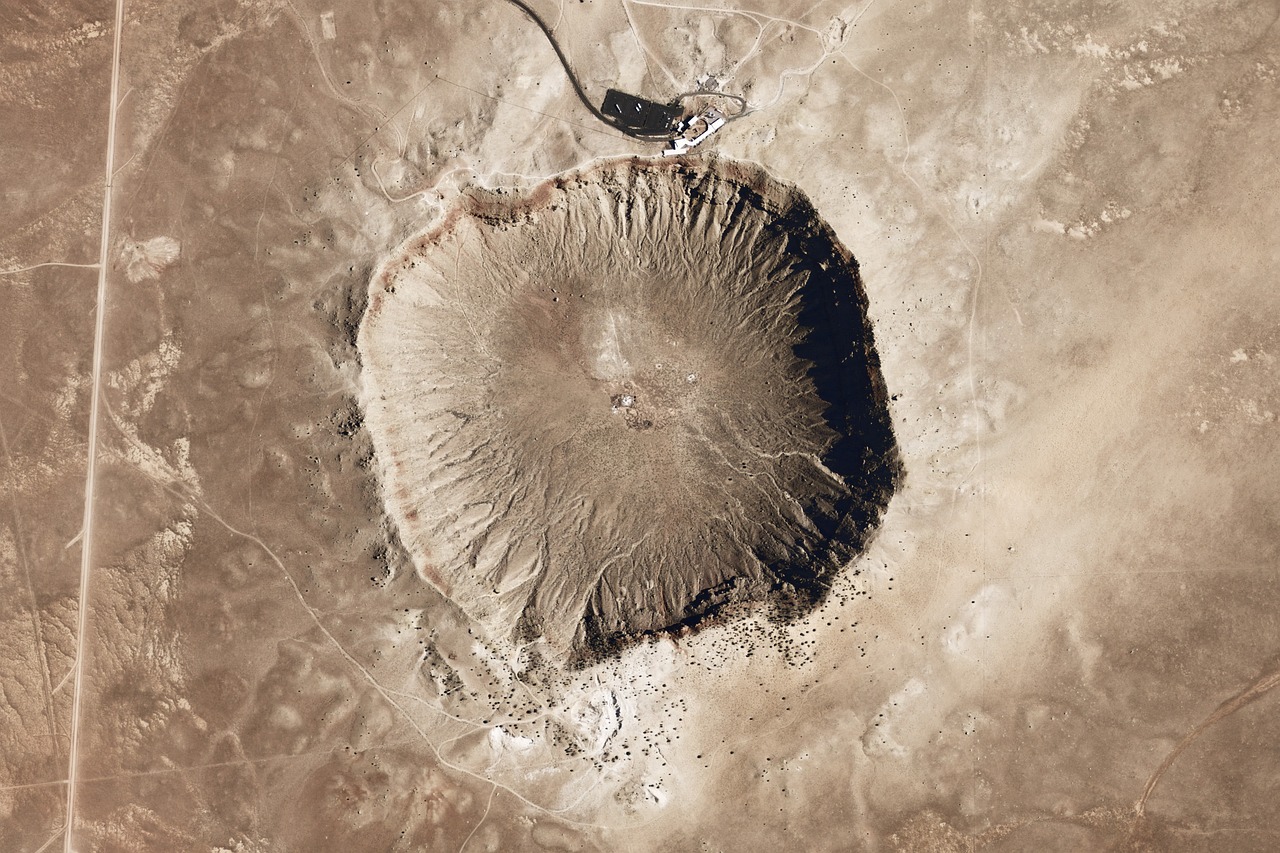

Size and Mass- Meteoroids can range in size from bitsy patches, lower than a grain of beach, to larger objects several measures in the periphery. still, utmost meteors that reach the Earth’s face as meteorites are fairly small, generally only a many centimeters in size. The mass of meteoroids can vary significantly, from lower than a gram to several tons.
Composition- Meteoroids are composed of colorful accouterments, including essence, silicate minerals, and organic composites. Their composition can give perceptivity to the conformation and elaboration of the solar system. The maturity of meteoroids is small, ranging from dust-sized patches to pebble-sized objects.
Decomposition and Vaporization- The violent heat generated during atmospheric entry causes meteoroids to suffer rapid-fire decomposition and vaporization. By the time most meteors come visible to spectators on the ground, they’ve disintegrated nearly entirely, turning into fine dust-sized patches.

Meteor Showers- Meteor showers occur when Earth passes through a trail of debris left by comets or asteroids. During these events, the rate of meteors entering the atmosphere increases, resulting in an advanced number of visible meteors. Meteor showers are frequently predictable and occur annually or at regular intervals.
Studying the characteristics of meteors helps astronomers understand the nature and composition of the objects within our solar system. It provides perceptivity into the origin and elaboration of asteroids, comets, and other Elysian bodies.